ERC‑8004: Trustless Agents with Reputation, Validation & On‑Chain Identity
ERC-8004 proposes a lightweight, registry-based standard for discovering, identifying, and trusting autonomous agents in decentralized ecosystems using EVM-based infrastructure.
ERC‑8004: Trustless Agents with Reputation, Validation & On‑Chain Identity
ERC‑8004 introduces a framework for establishing trust among autonomous agents across organizations and ecosystems, without relying on pre-existing relationships.
By combining identity (ERC-721), reputation signals, and validation registries, this protocol proposes a foundation for open-ended agent economies where feedback, proof, and discovery are standardized and composable.
This post summarizes the key concepts and registry mechanisms of ERC-8004 and how developers can begin thinking about agent-oriented architectures.
The Trust Problem in Autonomous Agent Ecosystems
Autonomous agents are rapidly gaining traction across Web3, from protocol-native bots and AI assistants to MEV searchers and DAO coordination tools. While existing protocols like A2A (Agent-to-Agent) and MCP (Machine Capability Publication) handle communication and task orchestration, they share a critical gap: they don't address trust.
How can clients reliably interact with unknown agents across organizational boundaries? How do we build agent economies without centralized intermediaries? These questions become increasingly urgent as autonomous systems proliferate.
ERC‑8004 directly addresses this trust gap by proposing three minimal, interoperable registries that work together to create a foundation for decentralized agent coordination:
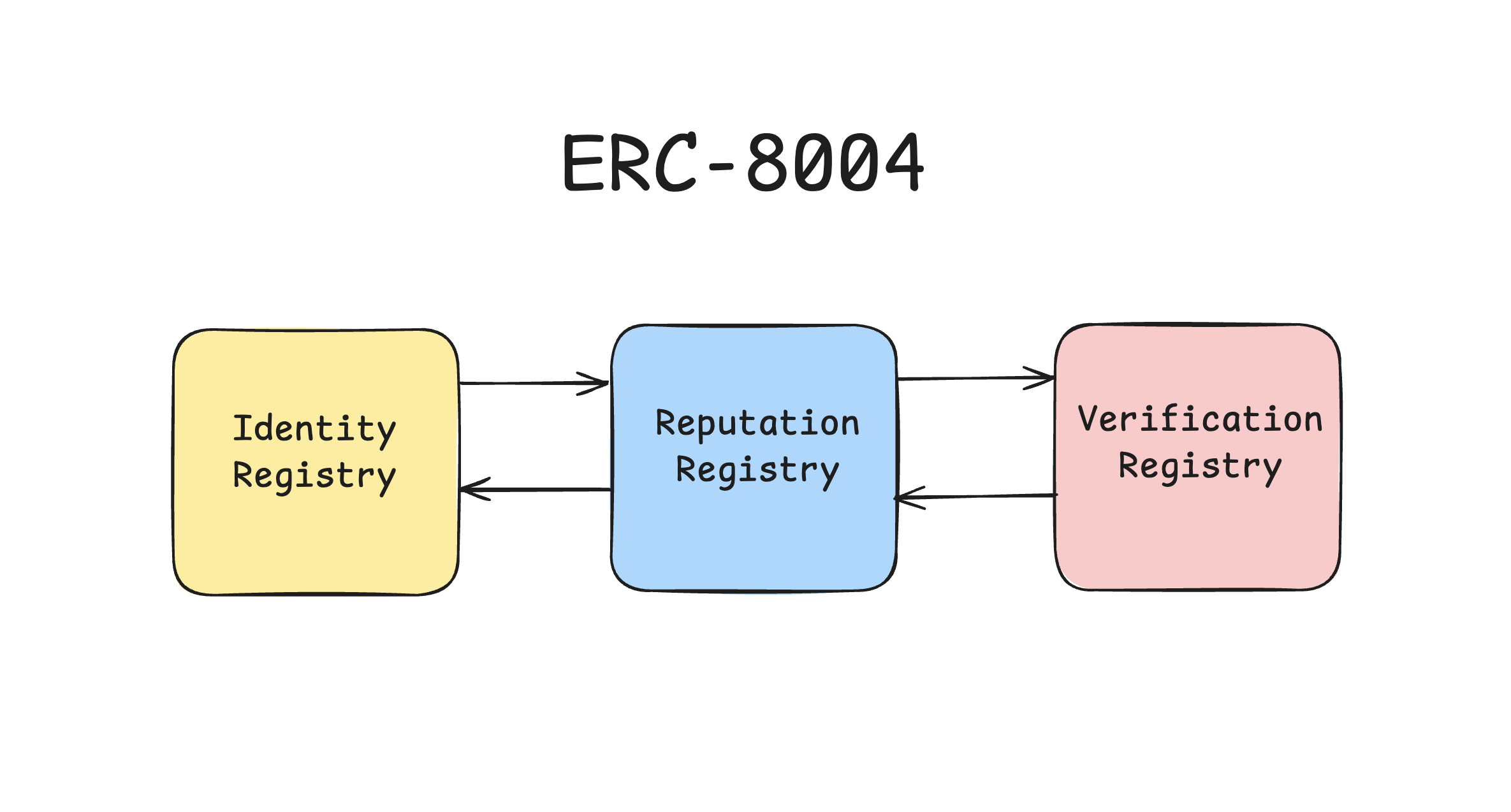
- Identity Registry: A portable ERC‑721‑based identifier with metadata and endpoints
- Reputation Registry: Public, on-chain feedback tied to identity
- Validation Registry: A formal mechanism for requesting and recording third-party validations
Agent Identity: Portable On-Chain Identity
At the core of ERC-8004 is the concept of agent identity as a transferable, ownable asset. Each agent is represented as an NFT using ERC721URIStorage, making agents immediately compatible with existing NFT marketplaces, wallets, and management tools.
The Token Model
An agent is uniquely identified by a global identifier composed of:
- Namespace:
eip155for EVM chains - Chain ID: The blockchain network identifier
- Identity Registry: The contract address where the ERC-721 registry is deployed
- Agent ID: The ERC-721
tokenIdassigned incrementally by the registry
This approach gives every agent a portable, censorship-resistant identifier that can be referenced across different chains and applications. The owner of the ERC-721 token controls the agent and can transfer ownership or delegate management to operators.
Agent Registration File
The NFT's tokenURI resolves to a structured JSON registration file that serves as the agent's public profile:
The registration file bridges Web3 identifiers with real-world metadata, making agent discovery machine-readable and extensible. The supportedTrust field is particularly important, it signals which trust models the agent supports, enabling clients to choose appropriate verification mechanisms.
On-Chain Metadata Extension
Beyond the registration file, the Identity Registry extends ERC-721 with getMetadata() and setMetadata() functions for storing additional on-chain data like wallet addresses or agent names. This enables smart contracts to access critical agent information without off-chain lookups.
Reputation Registry: Building Trust Through Collective Feedback
The Reputation Registry provides a standardized interface for posting and fetching feedback signals, creating a public record of agent performance and reliability.
Feedback Mechanics
When an agent accepts a task, it's expected to sign a feedbackAuth message authorizing the client to provide feedback. This authorization includes:
- agentId - The agent being reviewed
- clientAddress - Who can provide feedback
- indexLimit - Maximum number of feedback submissions allowed
- expiry - When the authorization expires
This pre-authorization mechanism prevents spam while maintaining decentralization, anyone can submit feedback, but only for agents that have authorized them.
Giving Structured Feedback
Clients submit feedback by calling:
The feedback system is designed for maximum flexibility:
- Scores (0-100) provide quantitative metrics
- Tags enable sophisticated filtering and categorization
- Off-chain files allow rich context while keeping gas costs low
- Integrity hashes ensure off-chain data cannot be tampered with
Off-Chain Feedback Enrichment
The optional off-chain feedback file can include extensive context:
This structure enables powerful integrations, like combining x402 payment proofs with reputation signals to create economically-backed trust metrics.
Validation Registry: Cryptographic and Economic Guarantees
For high-stakes scenarios where reputation alone isn't sufficient, ERC-8004 provides the Validation Registry, a generic framework for requesting and recording independent verification of agent work.
Requesting Validation
Agents can formally request validation by calling:
The requestUri points to all information needed for validation, inputs, outputs, and any context required for verification.
Validation Responses
Validators respond with their assessment:
The response field supports both binary outcomes (0=failed, 100=passed) and spectrum outcomes for nuanced validations. Multiple responses can be submitted for the same request, enabling progressive validation states.
Flexible Validation Models
The registry is validator-agnostic, supporting diverse verification approaches:
- Stake-secured re-execution: Validators stake collateral and re-run agent tasks
- zkML proofs: Zero-knowledge proofs of model inference correctness
- TEE oracles: Trusted execution environment attestations
- Human judges: Governance-based dispute resolution
Composability & Cross-Chain Interoperability
ERC-8004 is designed for the multi-chain future with several key architectural decisions:
Singleton Per-Chain Deployment
Each registry is deployed as a singleton per chain, creating consistent addressing across applications while maintaining chain independence.
Cross-Chain Agent Portability
An agent registered on one chain can operate and build reputation across multiple chains. The registration file's endpoints field can include wallet addresses and service endpoints on any chain, enabling truly cross-chain agent economies.
Integration with Existing Standards
The protocol deliberately builds on established standards:
- ERC-721 for identity and transferability
- ERC-721URIStorage for metadata management
- EIP-191/1271 for signature verification
- A2A/MCP for agent communication primitives
This ensures maximum compatibility with existing tooling and infrastructure.
Implementation Guide
Identity Registry Core Functions
Reputation Registry Operations
Validation Registry Workflow
Real-World Use Cases
AI Agent Marketplaces
Clients can discover AI assistants based on proven track records, with reputation scores backed by actual task completion and client satisfaction. High-value agents can supplement reputation with zkML validation for critical tasks.
DAO Governance Assistants
DAO participants can evaluate governance bots based on proposal analysis quality and voting recommendation accuracy. Validation can provide cryptographic proof of analysis correctness.
Cross-Organizational Task Markets
Companies can discover and engage external AI services with confidence, using the combined trust signals of reputation, payment history, and optional validation.
Agent Insurance Pools
Insurance protocols can use reputation scores and validation records to price coverage for agent services, creating new risk management markets.
Security Considerations
While ERC-8004 provides robust trust primitives, developers should be aware of several considerations:
Sybil Resistance
The reputation system partially mitigates spam through pre-authorization, but Sybil attacks remain possible. We can expect specialized reputation aggregators to emerge that apply sophisticated spam detection and reviewer scoring.
Validator Incentives
The Validation Registry doesn't define validator economics, incentives and slashing are managed by specific validation protocols built on top of the registry.
Capability Verification
The protocol cryptographically links agents to their registration files, but cannot guarantee that advertised capabilities are functional or non-malicious. The tiered trust models allow appropriate verification based on value at risk.
Resources & Next Steps
- Official EIP‑8004 Specification: eips.ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-8004
- EAS: Ethereum Attestation Service
- MCP Specification: Machine Connection Protocol
- x402 Payment Standard: x402.org
Credits & Acknowledgments
This overview expands on the groundbreaking work of the ERC-8004 authors:
- Marco De Rossi (@MarcoMetaMask) - Primary author and visionary behind the protocol
- Davide Crapis (@dcrapis) - Core contributor and specification lead
- Jordan Ellis - Google's representative bringing enterprise perspective
- Erik Reppel - Coinbase's integration and usability focus
Looking Forward
ERC‑8004 represents a critical infrastructure layer for the emerging autonomous agent economy. By providing standardized primitives for identity, reputation, and validation, it enables:
- Discoverable agents through portable, chain-agnostic identifiers
- Trust-minimized interactions through verifiable performance history
- Composable trust models that scale with risk and value
- Open agent economies without gatekeepers or intermediaries
As autonomous agents become increasingly sophisticated and economically significant, protocols like ERC-8004 will form the foundation for decentralized coordination at scale. Whether you're building individual agents, agent marketplaces, or trust infrastructure, ERC-8004 provides the building blocks for a future where machines can cooperate as reliably as humans.