A Deep Dive into ERC-7683 for Cross-Chain Intent
Blockchain interoperability is essential to communicating, transferring assets, and connecting across these diverse blockchain networks.
Introduction
The ecosystem has become more fragmented with the proliferation of multiple blockchains (rollups and appchains). Blockchain interoperability is essential to communicating, transferring assets, and connecting across these diverse blockchain networks.
Due to fragmented liquidity and interoperability issues, trading assets between different blockchains can be particularly challenging. ERC-7683 standard (draft) for cross-chain intents proposed by Uniswap Labs and Across is an interface for a cross-chain trade execution system. This standard aims to simplify cross-chain actions by providing a cohesive framework.
Here is a detailed overview of the standard for cross-chain intents and an analysis of how UniswapX brings cross-chain capability in swaps.
ERC-7683: A Unified Standard for Cross-Chain Intents
What is an Intent-based system?
A system that honors the “intention” of the user without worrying about the complexity of the process of execution. Cross-chain intents are when a user wants to act on one blockchain that results in an outcome on another blockchain.
Suppose Alice wants to trade her USDC on Ethereum for WETH on an L2. Traditionally, Alice would have to go through multiple steps including using bridges, and different wallets, making it complex and time-consuming.
With ERC-7683, Alice doesn’t need to take multiple steps or worry about how it happens. Intents-based systems simply allow users to specify the end state of the chain – and a network of fillers compete to fulfill the user’s outcome as fast and cheaply as possible.
What Problem Does ERC-7683 Solve?
Many intent-based systems rely on their own network of fillers, leading to a single point of failure and centralization risks. As intent-based systems grow, managing separate relayers and fillers for each protocol becomes challenging.
The ERC-7683 standard addresses these issues by standardizing cross-chain intents, enabling a universal filler network for more efficient transactions and making it easier for different systems to work together.
Key Components in Cross-chain Trade Execution with ERC7683
A. Swapper (user): The one who signs an off-chain message defining the order with CrossChainOrder Struct, which contains all the necessary information about an order for the cross-chain trade.
Additionally, ResolvedCrossChainOrder struct provides detailed information about the order, making it easier to compute the necessary inputs and outputs for fulfilling the order.
B. Filler: Fillers are entities or smart contracts responsible for initiating trades on the origin chain, executing orders on the destination chain, and settling cross-chain orders.
C. Settlement Contract: The ISettlementContract interface defines the basic structure for settlement contract functions such as initiate and resolve.
How can ERC-7683 be used in other systems for Cross-chain functionality?
By extending ISettlementContract, you can implement ERC-7683 for cross-chain orders specific to any protocol. Here is an example of implementation using Permit2 and Across:
- Alice creates a cross-chain order signed with Permit2.
- Settlement contract verifies and processes the order.
- Filler resolves order and prepares USDC.
- Filler calls
fillCrossChainOrderto fulfill the order and transfer USDC.
Benefits of ERC-7683
- Interoperability: Seamless interaction between networks.
- Better User Experience: Simplifies cross-chain transactions.
- Lower Entry Barriers and Costs: Reduced complexity and costs.
- Broader Access: Extensive filler network improves efficiency.
UseCase: UniswapX for Cross-Chain Trades
In July 2023, Uniswap introduced UniswapX for cross-chain functionality, integrating ERC-7683 into Uniswap's ecosystem.
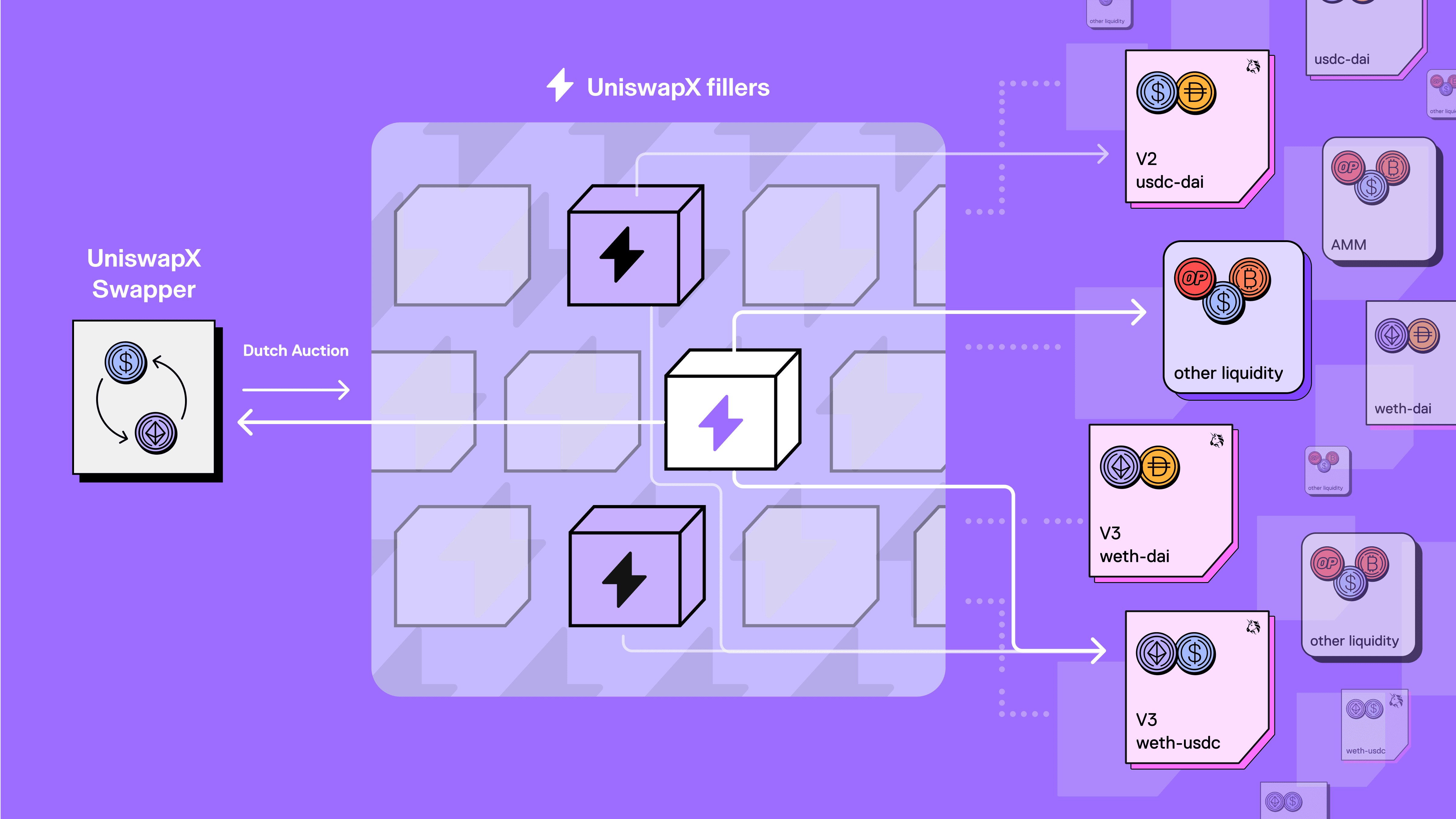 Image Source: Uniswap Blog
Image Source: Uniswap Blog
UniswapX is an auction-based protocol, using Dutch auctions where fillers bid to offer the best price.
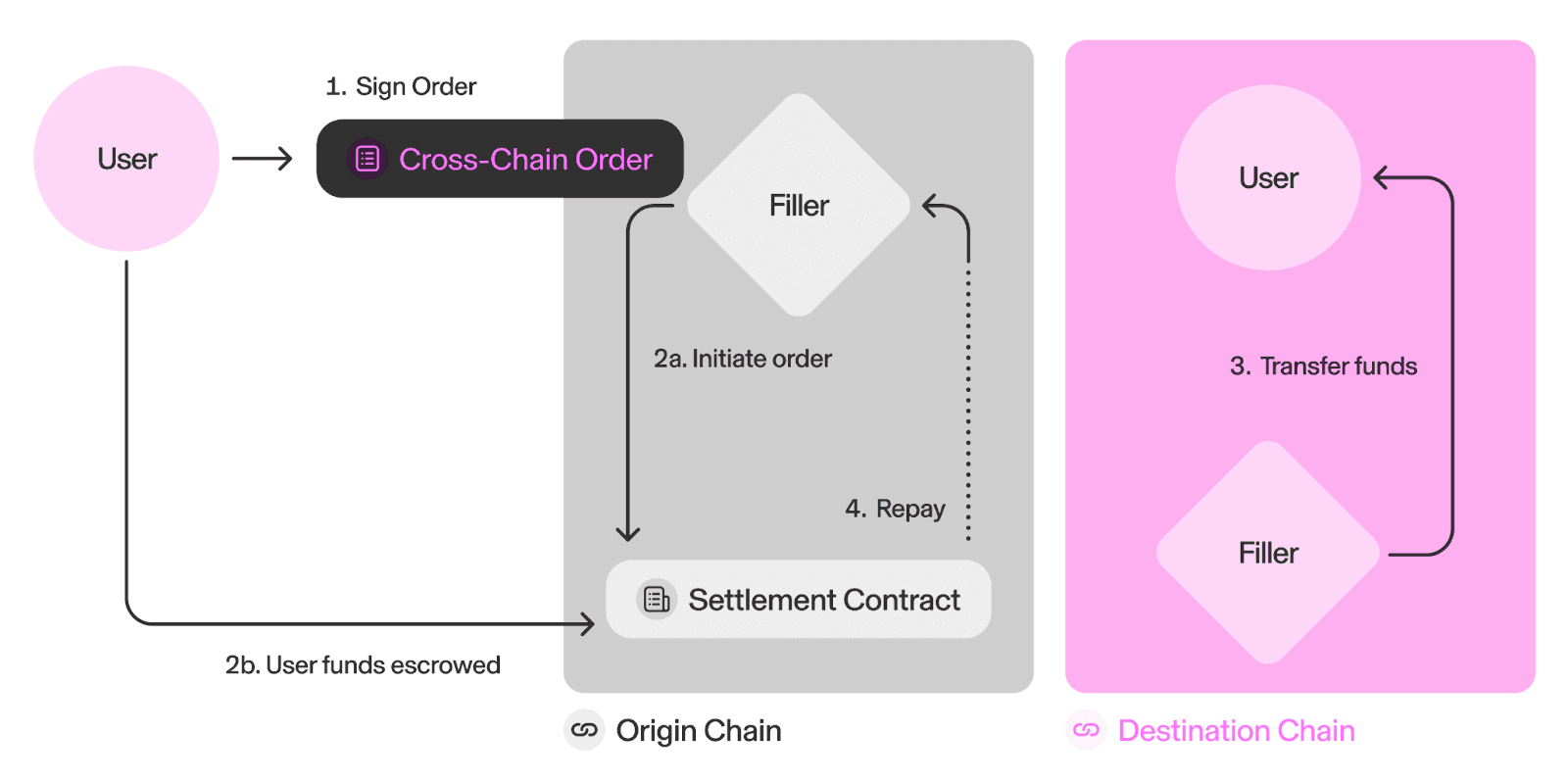 Image Source: Uniswap Twitter
Image Source: Uniswap Twitter
- Alice creates a
CrossChainOrderon UniswapX. - Fillers bid in a Dutch auction.
- Alice selects best price and initiates the order.
- Filler executes trade cross-chain and resolves.
- Tokens transferred according to
ResolvedCrossChainOrder.
Conclusion
ERC-7683 simplifies cross-chain trading by providing a unified standard, enhancing interoperability, liquidity, reducing costs, and creating a more efficient ecosystem.
About BuildBear
BuildBear is tailored for DApp development and testing. Build personalized Private Testnet sandboxes across blockchain networks, mint unlimited tokens, and leverage rapid transaction speeds (under 3 seconds). Equipped with tools for real-time testing and debugging, BuildBear streamlines blockchain development.